

|
EIDORS: Electrical Impedance Tomography and Diffuse Optical Tomography Reconstruction Software |
|
EIDORS
(mirror) Main Documentation Tutorials − Image Reconst − Data Structures − Applications − FEM Modelling − GREIT − Old tutorials − Workshop Download Contrib Data GREIT Browse Docs Browse SVN News Mailing list (archive) FAQ Developer
|
Noise performance of different hyperparameter selection approachesThis tutorial presents different approaches used to select the hyperparameter with the goal to achieve an identical noise performance between different measurement configurations (i.e. electrode position, skip of meas/stim pattern, etc.).We show the effect of different measurement configurations for the following four hyperparameter selection approaches:
Human thorax model with different electrode configurationsFirst, we load the human thorax model, assign realistic conductivity values and generate a conductivity change in the left lung (10% increase) and right lung (5% increase).We generate the following four different model configurations in order to show how each hyperparameter selection approach is influenced by the electrode position and number, and the skip (number of inactive electrodes in between the two injecting current/measuring voltage):
% create forward models of the human thorax
% $Id: noise_performance_01.m 5424 2017-04-25 17:45:19Z aadler $
% generate base model for forward solving
fmdl = mk_library_model('adult_male_32el_lungs');
imgBasic = mk_image(fmdl, 0.2); % back ground conductivity
imgBasic.elem_data(fmdl.mat_idx{2}) = 0.13; % left lung
imgBasic.elem_data(fmdl.mat_idx{3}) = 0.13; % right lung
imgBasic.elem_data1 = imgBasic.elem_data;
% now generate a conductivity change
imgBasic.elem_data2 = imgBasic.elem_data;
imgBasic.elem_data2(fmdl.mat_idx{2}) = 0.1 * imgBasic.elem_data2(fmdl.mat_idx{2});
imgBasic.elem_data2(fmdl.mat_idx{3}) = 0.05 * imgBasic.elem_data2(fmdl.mat_idx{3});
% generate base model for inverse model
rmdlBasic = mk_library_model('adult_male_32el');
% 16 electrodes, equidistantly spaced, skip 0 (adjacent) stim/meas pattern
imgs{1} = imgBasic;
rmdls{1} = rmdlBasic;
imgs{1}.fwd_model.electrode(2:2:end) = [];
imgs{1}.fwd_model.name = '16 elecs, skip 0';
rmdls{1}.electrode(2:2:end) = [];
imgs{1}.fwd_model.stimulation = mk_stim_patterns(16,1,[0,1],[0,1],{'no_rotate_meas','no_meas_current'});
rmdls{1}.stimulation = imgs{1}.fwd_model.stimulation;
% 16 electrodes, equidistantly spaced, stim/meas pattern with skip=5
imgs{2} = imgBasic;
rmdls{2} = rmdlBasic;
imgs{2}.fwd_model.electrode(2:2:end) = [];
imgs{2}.fwd_model.name = '16 elecs, skip 5';
rmdls{2}.electrode(2:2:end) = [];
imgs{2}.fwd_model.stimulation = mk_stim_patterns(16,1,[0,1+5],[0,1+5],{'no_rotate_meas','no_meas_current'});
rmdls{2}.stimulation = imgs{2}.fwd_model.stimulation;
% 32 electrodes, equidistantly spaced, skip 0 (adjacent) stim/meas pattern
imgs{3} = imgBasic;
rmdls{3} = rmdlBasic;
imgs{3}.fwd_model.name = '32 elecs, skip 0';
imgs{3}.fwd_model.stimulation = mk_stim_patterns(32,1,[0,1],[0,1],{'no_rotate_meas','no_meas_current'});
rmdls{3}.stimulation = imgs{3}.fwd_model.stimulation;
% 24 electrodes, more densly spaced ventrally, stim/meas pattern with skip=9
imgs{4} = imgBasic;
rmdls{4} = rmdlBasic;
imgs{4}.fwd_model.electrode(9:2:24) = []; % remove every 2nd elec on the back
rmdls{4}.electrode(9:2:24) = [];
imgs{4}.fwd_model.name = '24 elecs, skip 9';
imgs{4}.fwd_model.stimulation = mk_stim_patterns(24,1,[0,1+9],[0,1+9],{'no_rotate_meas','no_meas_current'});
rmdls{4}.stimulation = imgs{4}.fwd_model.stimulation;
% now plot every model
clf;
for ii = 1:length(imgs)
subplot(1,4,ii);
h = show_fem(imgs{ii});
set(h, 'edgecolor', 'none');
title(imgs{ii}.fwd_model.name);
view(2);
set(gca, 'ytick', [], 'xtick', []);
xlabel('Dorsal');
ylabel('Right');
end
print_convert np_models.png '-density 100'
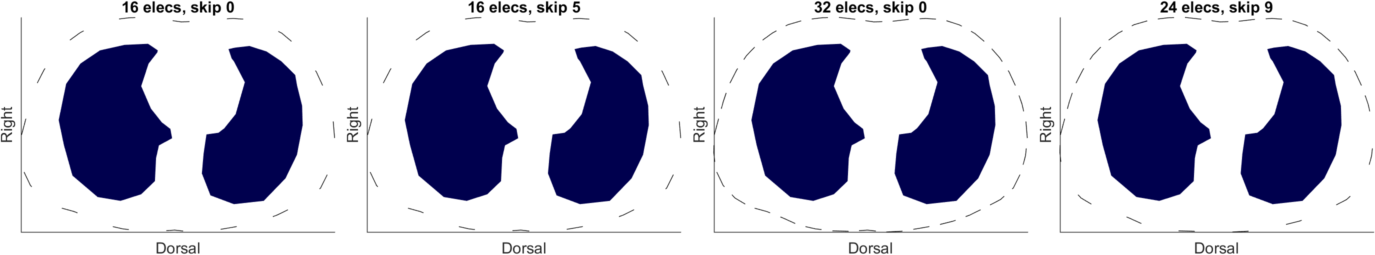
Figure: The four different configurations electrode / skip configurations used in the analysis. Generating EIT voltage measurements and noise
% generate noisy EIT voltage measurements
% $ Id: $
for ii = 1:length(imgs)
imgs{ii}.elem_data = imgs{ii}.elem_data1;
vh{ii} = fwd_solve(imgs{ii});
imgs{ii}.elem_data = imgs{ii}.elem_data2;
vi{ii} = fwd_solve(imgs{ii});
end
% generate additive white Gaussian noise
NOISE_N_REALIZATIONS = 1E3;
NOISE_AMPLITUDE = 5E-3;
noise = NOISE_AMPLITUDE * randn(32*32, NOISE_N_REALIZATIONS);
Visualizing noise performanceIterate over
% create reconstruction models and select hyperparameter with different approaches
% $Id: noise_performance_03.m 5760 2018-05-20 10:52:41Z aadler $
if ~exist('rms'); rms = @(n,dim) sqrt(mean(n.^2,dim)); end % define @rms if toolbox not avail
for recon_approach = {'GREIT','GN'}
switch recon_approach{1}
case 'GREIT';
lambda_sel_approach = {'NF', 'SNR', 'LCC', 'GCV'};
imdl_creation_fun = @(img, opts, lambda) mk_GN_model(img, opts, lambda);
case 'GN';
lambda_sel_approach = {'NF', 'SNR'};
imdl_creation_fun = @(img, opts, lambda) mk_GREIT_model(img, 0.2, lambda, opts);
otherwise; error('unspecified recon_approach');
end
clf;
for jj = 1:length(lambda_sel_approach)
for ii = 1:length(imgs)
subplot(length(lambda_sel_approach), 4, ii + (jj-1)*length(imgs));
opts = [];
opts.img_size = [32 32];
switch(lambda_sel_approach{jj})
case 'NF' % fixed noise figure
lambda = [];
opts.noise_figure = 0.5;
case 'SNR' % fixed image SNR as suggested by Braun et al.
lambda = 1; % lambda is used as initial weight to find the appropriate SNR
% this is an arbitrary initial guess to avoid non-convergence
opts.image_SNR = imdl{1,1}.SNR; % same as NF=0.5 for 16 elecs adjacent
case 'LCC' % LCC: L-curve criterion
lambda = 1; % lambda will be selected further below
case 'GCV' % GCV: generalized-cross validation
lambda = 1; % lambda will be selected further below
otherwise
error(['Unknown hyperparameter selection approach: ', lambda_sel_approach(jj)]);
end
% create reconstruction framework
imdl{jj, ii} = imdl_creation_fun(mk_image(rmdls{ii},1), opts, lambda);
imdl{jj, ii}.fwd_model.name = imgs{ii}.fwd_model.name;
% add noise to inhomogeneous conductivity change
vn = repmat(vi{ii}.meas, 1, size(noise,2)) + noise(1:length(vi{ii}.meas), :);
if strcmp(lambda_sel_approach{jj}, 'LCC') || strcmp(lambda_sel_approach{jj}, 'GCV')
% use simulated noisy data to choose hyperparameter either with:
% LCC: L-curve criterion
% GCV: generalized-cross validation
lambdas = calc_lambda_regtools(imdl{jj, ii}, vh{ii}.meas, vn, lambda_sel_approach{jj});
imdl{jj, ii}.hyperparameter.value = median(lambdas);
end
% calulate image SNR for each approach
imdl{jj, ii}.SNR = calc_image_SNR(imdl{jj, ii});
% perform image reconstruction
imgr{jj, ii} = inv_solve(imdl{jj, ii}, vh{ii}.meas, vn);
% calulate temporal RMS image as in Braun et al., 2017, IEEE TBME
trmsa{jj, ii} = imgr{jj, ii};
trmsa{jj, ii}.elem_data = rms(trmsa{jj, ii}.elem_data, 2);
% normalize to maximal amplitude
norm_value = max(trmsa{jj, ii}.elem_data);
trmsa{jj, ii}.elem_data = trmsa{jj, ii}.elem_data / norm_value;
imgr{jj, ii}.elem_data = imgr{jj, ii}.elem_data / norm_value;
% force displaying values in range [0 1]
trmsa{jj, ii}.calc_colours.clim = 0.5;
trmsa{jj, ii}.calc_colours.ref_level = 0.5;
trmsa{jj, ii}.calc_colours.cmap_type = 'greyscale';
imgr{jj, ii}.calc_colours.clim = 1;
imgr{jj, ii}.calc_colours.ref_level = 0;
% show tRMSA image for each configuration
h = show_fem(trmsa{jj, ii}, 1);
set(h, 'edgecolor', 'none');
title([num2str(ii, '(%01d)'), ' ', lambda_sel_approach{jj}, ': ', imdl{jj, ii}.fwd_model.name]);
set(gca, 'ytick', [], 'xtick', []);
if ii == 1
ylabel({['(', char(double('a')+jj-1), ') ', lambda_sel_approach{jj}], 'Right'});
else
ylabel('Right');
end
xlabel({'Dorsal', sprintf('SNR = %03.2d, \\lambda = %03.2d', imdl{jj, ii}.SNR, imdl{jj, ii}.hyperparameter.value)});
end
end
opt.resolution = 200;
opt.vert_space = 20;
opt.pagesize = [16,8];
switch recon_approach{1}
case 'GREIT'; print_convert('np_trmsa_GREIT.png',opt)
case 'GN'; print_convert('np_trmsa_GN.png',opt);
otherwise; error('unspecified recon_approach');
end
end %for recon_approach = {'GREIT','GN'}
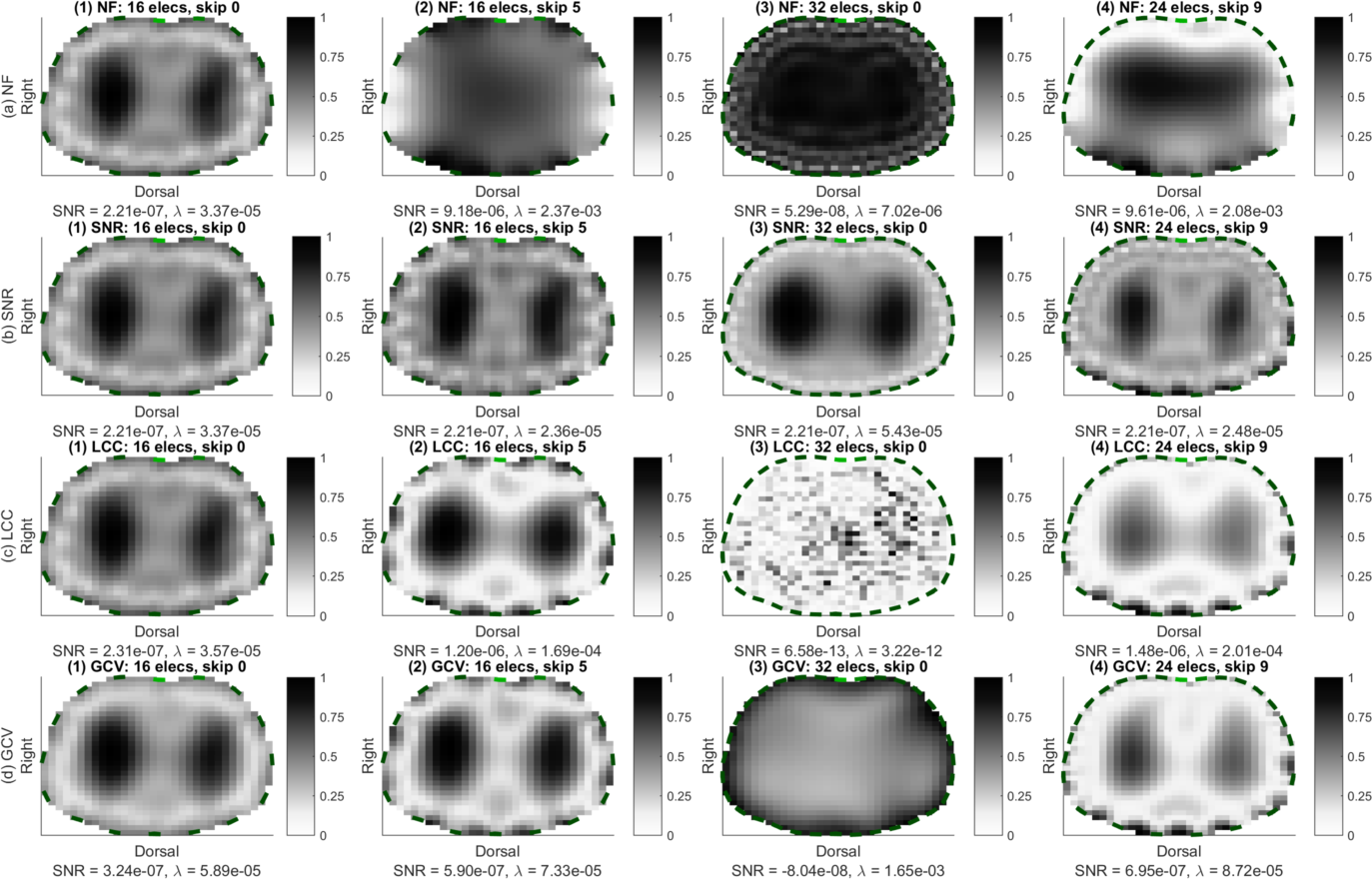
Figure: Gauss Newton reconstruction: temporal RMS amplitude (TRMSA) images of the same conductivity change in the lungs with identical noise for different measurement configurations (1) to (4) and different hyperparameter selection approaches: (a) a fixed noise figure (NF = 0.5), (b) a fixed SNR = 2.21E-07 (equal to NF = 0.5 for the 1st configuration), (c) L-curve criterion (LCC), and (d) generalized cross-validation (GCV). 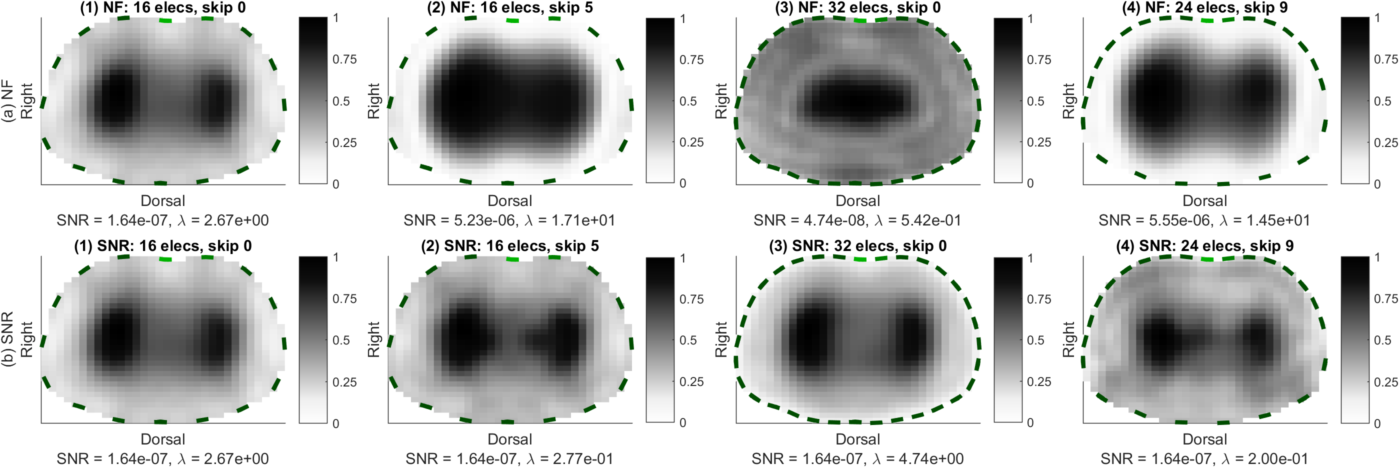
Figure: GREIT reconstruction: temporal RMS amplitude (TRMSA) images of the same conductivity change in the lungs with identical noise for different measurement configurations (1) to (4) and different hyperparameter selection approaches: (a) a fixed noise figure (NF = 0.5), and (b) a fixed SNR = 2.21E-07 (equal to NF = 0.5 for the 1st configuration). Last Modified: $Date: 2018-05-20 06:55:01 -0400 (Sun, 20 May 2018) $ by $Author: aadler $ |