

|
EIDORS: Electrical Impedance Tomography and Diffuse Optical Tomography Reconstruction Software |
|
EIDORS
(mirror) Main Documentation Tutorials − Image Reconst − Data Structures − Applications − FEM Modelling − GREIT − Old tutorials − Workshop Download Contrib Data GREIT Browse Docs Browse SVN News Mailing list (archive) FAQ Developer
|
GREIT Test ParametersDuring the GREIT development process, we developed a set of figures of merit to characterize the performance of an algorithm.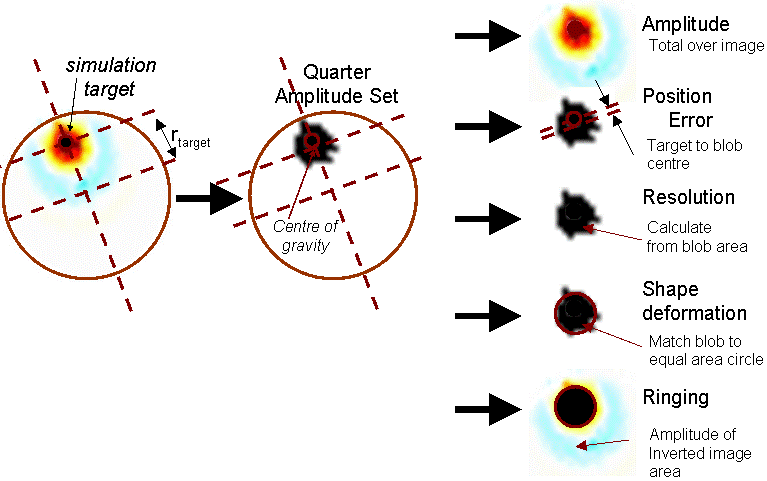
Figure: GREIT test parameters: Amplitude (AR), Position Error (PE), Resolution (RES), Shape Deformation (SD), Ringing (RNG) Simulate 3D object
% Simulate obj $Id: GREIT_test_params01.m 2167 2010-04-04 21:39:48Z aadler $
fmdl = ng_mk_cyl_models([2,1,0.08],[16,1],[0.05]);
fmdl.stimulation = mk_stim_patterns(16,1,[0,1],[0,1],{},1);
imgs= mk_image( fmdl, 1);
show_fem(imgs);
print_convert('GREIT_test_params01a.png','-density 60');
view(0,0)
xlim([-.4,.4])
zlim(1+[-.4,.4])
print_convert('GREIT_test_params01b.png','-density 60');
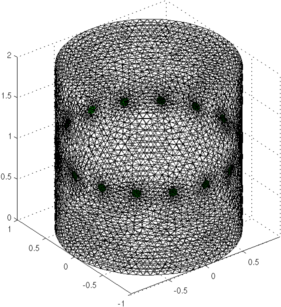
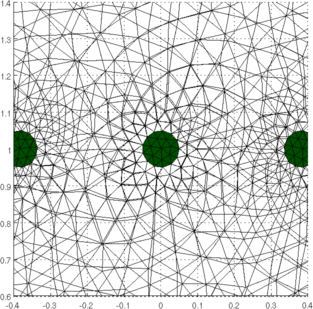
Figure: Simulation Mesh (right) and close-up of the electrodes (left) Simulate Sequence of Targets
% Simulate obj $Id: GREIT_test_params02.m 4823 2015-03-29 15:17:16Z bgrychtol-ipa $
% Specify positions to simulate (only x-axis here)
r = linspace(0,0.9,100);
xyzr = [r; zeros(1,100); ones(1,100);
0.05*ones(1,100)];
[vh,vi] = simulate_movement(imgs, xyzr);
% Show GREIT images
opt.noise_figure = 0.5;
i_gr = mk_GREIT_model(fmdl,0.2,[],opt);
imgr = inv_solve(i_gr, vh, vi(:,1:5:100));
imgr.show_slices.img_cols = 5;
show_slices(imgr);
print_convert('GREIT_test_params02a.png','-density 60');
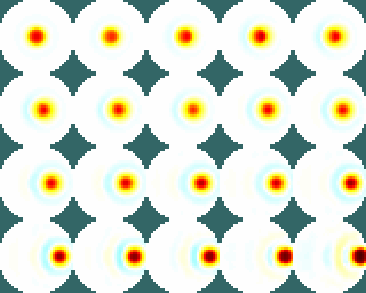
Figure: Illustration of the object locations in the simulation Calculate the parametersImage Reconstruction
% GREIT params eval $Id: GREIT_test_params03.m 2240 2010-07-04 14:41:32Z aadler $
% Reconstruct GREIT Images
imdl_gr = mk_common_gridmdl('GREITc1');
imgc{1} = inv_solve(imdl_gr, vh, vi);
% Reconstruct backprojection Images
imdl_bp = mk_common_gridmdl('backproj');
imgc{2} = inv_solve(imdl_bp, vh, vi);
fname_base = 'GREIT_test_params04';
Calculate performance
% GREIT params eval $Id: GREIT_test_params04.m 2240 2010-07-04 14:41:32Z aadler $
for i= 1:length(imgc);
imgr = imgc{i};
imgr.calc_colours.npoints = 32;
params = eval_GREIT_fig_merit(imgr, xyzr);
fname = sprintf('%s%c', fname_base, i+'a'-1);
plot(r, params(1,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,2.0]); ylabel('AR');
print_convert([fname,'_ar.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(2,:)); axis([0,0.9,-0.15,0.15]); ylabel('PE');
print_convert([fname,'_pe.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(3,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,0.4]); ylabel('RES');
print_convert([fname,'_res.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(4,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,0.3]); ylabel('SD');
print_convert([fname,'_sd.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(5,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,0.6]); ylabel('RNG');
print_convert([fname,'_rng.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
end
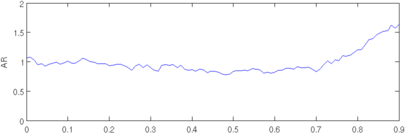 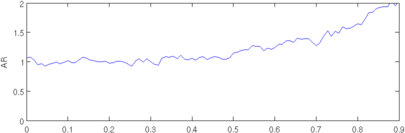 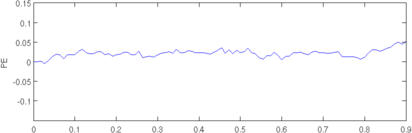 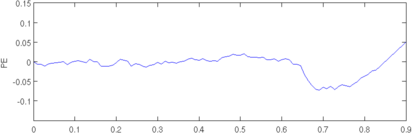 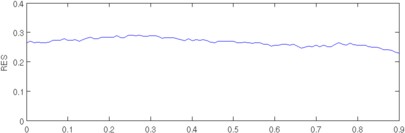 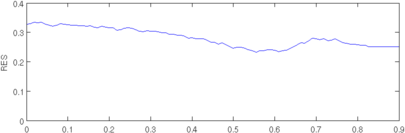 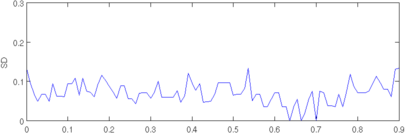 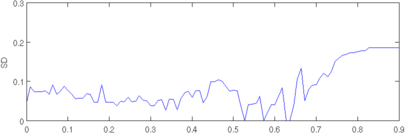 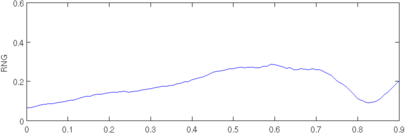 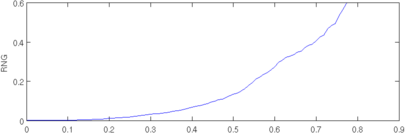 Figure: Evaluation of GREIT (right), and Sheffield Backprojection (left) GREIT parameters AR, PE, RES, SD, and RNG as a function of point radial position CommentThere are several issues with this measurement, that should be kept in mind. This is an example of the use of the function, not a specification.
Simulate Sequence of Targets above the plane (×25%)
% Simulate obj $Id: GREIT_test_params05.m 2167 2010-04-04 21:39:48Z aadler $
% Simulate positions that are 0.25 above the plane
r = linspace(0,0.9,100);
xyzr = [r;
zeros(1,100);
1.25*ones(1,100);
0.05*ones(1,100)];
[vh,vi] = simulate_movement(imgs, xyzr);
% Show GREIT images
i_gr = mk_common_gridmdl('GREITc1');
imgr = inv_solve(i_gr, vh, vi(:,1:5:100));
imgr.show_slices.img_cols = 5;
show_slices(imgr);
print_convert('GREIT_test_params05a.png','-density 60');
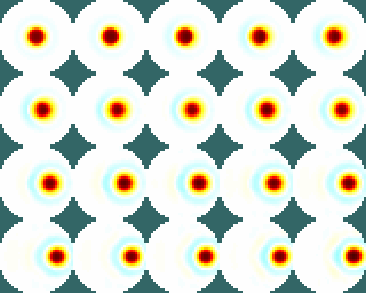
Figure: Illustration of the object locations in the simulation Calculate the parameters
% GREIT params eval $Id: GREIT_test_params06.m 2240 2010-07-04 14:41:32Z aadler $
% Reconstruct GREIT Images
imdl_gr = mk_common_gridmdl('GREITc1');
imgc{1} = inv_solve(imdl_gr, vh, vi);
% Reconstruct backprojection Images
imdl_bp = mk_common_gridmdl('backproj');
imgc{2} = inv_solve(imdl_bp, vh, vi);
fname_base = 'GREIT_test_params06';
% GREIT params eval $Id: GREIT_test_params04.m 2240 2010-07-04 14:41:32Z aadler $
for i= 1:length(imgc);
imgr = imgc{i};
imgr.calc_colours.npoints = 32;
params = eval_GREIT_fig_merit(imgr, xyzr);
fname = sprintf('%s%c', fname_base, i+'a'-1);
plot(r, params(1,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,2.0]); ylabel('AR');
print_convert([fname,'_ar.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(2,:)); axis([0,0.9,-0.15,0.15]); ylabel('PE');
print_convert([fname,'_pe.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(3,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,0.4]); ylabel('RES');
print_convert([fname,'_res.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(4,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,0.3]); ylabel('SD');
print_convert([fname,'_sd.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
plot(r, params(5,:)); axis([0,0.9,0,0.6]); ylabel('RNG');
print_convert([fname,'_rng.png'], '-density 60',0.3);
end
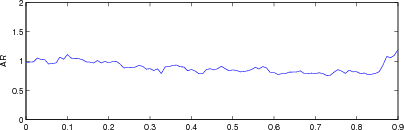 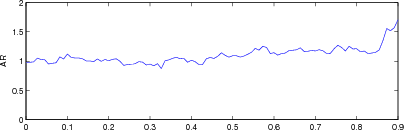 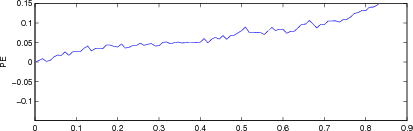 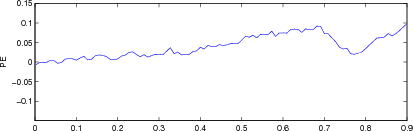 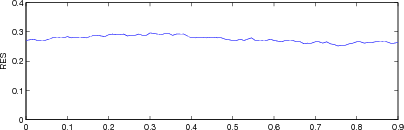 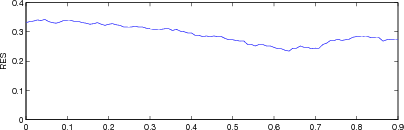 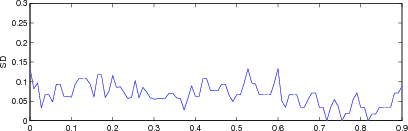 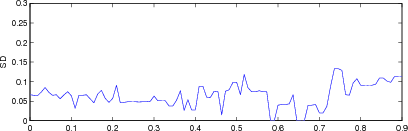 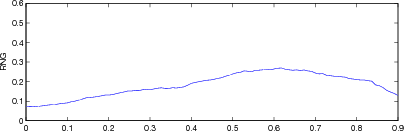 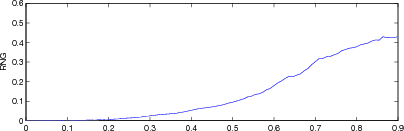 Figure: Evaluation for off plane object (25%) of GREIT (left), and Sheffield Backprojection (right) GREIT parameters AR, PE, RES, SD, and RNG as a function of point radial position |
Last Modified: $Date: 2017-02-28 13:12:08 -0500 (Tue, 28 Feb 2017) $ by $Author: aadler $