

|
EIDORS: Electrical Impedance Tomography and Diffuse Optical Tomography Reconstruction Software |
|
EIDORS
(mirror) Main Documentation Tutorials − Image Reconst − Data Structures − Applications − FEM Modelling − GREIT − Old tutorials − Workshop Download Contrib Data GREIT Browse Docs Browse SVN News Mailing list (archive) FAQ Developer
|
EIDORS fwd_modelsComplete electrode model (CEM) convergence study using higher order finite elements methods (FEM)The implementation of high order finite elements for the CEM, the following convergence study of CEM and the "semi-analytic" solution to test convergence, are described in detail in the following:
Methods and ResultsCarefully create an FEM of CEM on a square domain on which a "semi-analytic" solution can be determined so that we can rigorously study how errors in the forward problem of EIT vary with contact impedance, mesh refinement and approximation order in different norms.
nmesh = 3; %greater or equal 4 for sensible rate estimates (depends on computer architec)
%Build a square CEM model
%Nodal coordinates and electrode nodes
x=linspace(0,pi,6);
y=linspace(0,pi,6);
[X,Y]=meshgrid(x,y); vtx=[X(:) Y(:)];
elec_nodes={[0 0],[0,pi]};
mdl=mk_fmdl_from_nodes(vtx,elec_nodes,0.02,'name');
%Electrode node indices and nodes on boundary not on elecs
mdl.electrode(1).nodes = [7,13];
mdl.electrode(2).nodes = [19,25];
bound_nodes_not_elecs = [1,2,3,4,5,6,12,18,24,30,31,32,33,34,35,36];
%Make image and add some fields
img=mk_image(mdl,1); %figure; show_fem(img);
stim = mk_stim_patterns(2,1,'{ad}','{ad}',{'meas_current'}, 1);
mdl.stimulation=stim;
img.fwd_model.bound_nodes_not_elecs=bound_nodes_not_elecs;
mdl.bound_nodes_not_elecs=bound_nodes_not_elecs;
img.fwd_model.stimulation=stim; img.fwd_solve.get_all_meas=1;
mdl_init=mdl;
%Copy model, assign unit conductivity and plot
mdl_h1=mdl; img_h1=mk_image(mdl_h1,1);
figure;
subplot(121); show_fem(img_h1); hold on;
plot(img_h1.fwd_model.nodes(bound_nodes_not_elecs,1),...
img_h1.fwd_model.nodes(bound_nodes_not_elecs,2),'r*');
xlab = xlabel('x'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('y'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
%Refine model
mdl_h2=h_refine_square_domain(mdl); img_h2=mk_image(mdl_h2,1);
subplot(122); show_fem(img_h2); hold on;
plot(img_h2.fwd_model.nodes(bound_nodes_not_elecs,1),...
img_h2.fwd_model.nodes(bound_nodes_not_elecs,2),'r*');
xlab = xlabel('x'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('y'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance01a.png
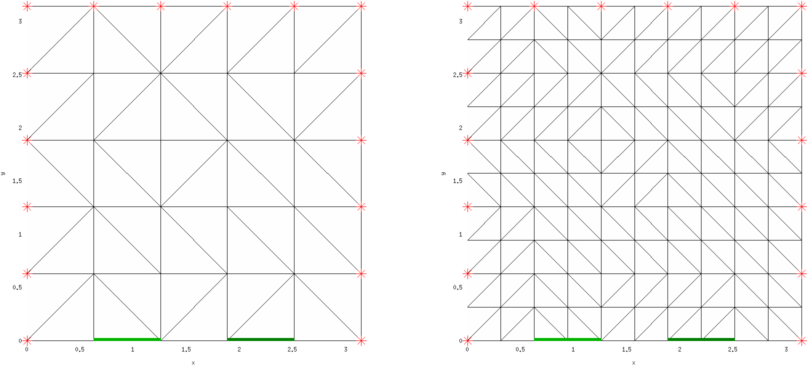
Figure: Initial 3D finite element model (left) and the same model after a single uniform h-refinement. The CEM electrodes (to drive voltage) are green lines and the (point) voltage measurement electrodes are red crosses.
%Loop over contact impedances
z_c=[0.00001,0.0001,0.001,0.01,0.1,1,10,100,1000];
for z_cj=1:length(z_c) % z_c=[0.1,1000];
%Reinitialise model and make image
mdl=mdl_init; img=mk_image(mdl,1);
mdl.electrode(1).z_contact = z_c(z_cj);
img.fwd_model.electrode(1).z_contact=z_c(z_cj);
mdl.electrode(2).z_contact = z_c(z_cj);
img.fwd_model.electrode(2).z_contact=z_c(z_cj);
%Solve forward problem with linear, quadratic, cubic and find H1-error
tic;
fprintf(1,'H1 Lin');
[lin_errL2(1,z_cj),lin_errH1(1,z_cj),lin_errH1tot(1,z_cj),lin_errI(1,z_cj), ...
lin_errUS(1,z_cj),lin_errUM(1,z_cj),lin_errUSM(1,z_cj), ...
lin_timing_solver(1,z_cj),lin_DOF(1,z_cj)]= calc_error_norms_for_square_domain(img,'tri3',1);
toc;
tic;
fprintf(1,'H1 Quad');
[quad_errL2(1,z_cj),quad_errH1(1,z_cj),quad_errH1tot(1,z_cj),quad_errI(1,z_cj), ...
quad_errUS(1,z_cj),quad_errUM(1,z_cj),quad_errUSM(1,z_cj), ...
quad_timing_solver(1,z_cj),quad_DOF(1,z_cj)]= calc_error_norms_for_square_domain(img,'tri6',1);
toc;
tic; fprintf(1,'H1 Cub');
[cub_errL2(1,z_cj),cub_errH1(1,z_cj),cub_errH1tot(1,z_cj),...
cub_errI(1,z_cj),cub_errUS(1,z_cj),cub_errUM(1,z_cj),cub_errUSM(1,z_cj),cub_timing_solver(1,z_cj),...
cub_DOF(1,z_cj)]=calc_error_norms_for_square_domain(img,'tri10',1); toc;
%Loop over different refinements
for ii=1:nmesh-1
%Refine model uniformly and find errors with lin, quad, cubic
mdl=h_refine_square_domain(mdl); img=mk_image(mdl,1);
tic; fprintf(1,'H1 Lin');
[lin_errL2(ii+1,z_cj),lin_errH1(ii+1,z_cj),...
lin_errH1semi(ii+1,z_cj),lin_errI(ii+1,z_cj),lin_errUS(ii+1,z_cj),lin_errUM(ii+1,z_cj),...
lin_errUSM(ii+1,z_cj),lin_timing_solver(ii+1,z_cj),lin_DOF(ii+1,z_cj)]=...
error_2D_squ_CEM(img,'tri3',0); toc;
tic; fprintf(1,'H1 Quad');
[quad_errL2(ii+1,z_cj),quad_errH1(ii+1,z_cj),...
quad_errH1semi(ii+1,z_cj),quad_errI(ii+1,z_cj),quad_errUS(ii+1,z_cj),quad_errUM(ii+1,z_cj),...
quad_errUSM(ii+1,z_cj),quad_timing_solver(ii+1,z_cj),quad_DOF(ii+1,z_cj)] = ...
error_2D_squ_CEM(img,'tri6',0); toc;
tic; fprintf(1,'H1 Cub');
[cub_errL2(ii+1,z_cj),cub_errH1(ii+1,z_cj),cub_errH1semi(ii+1,z_cj),...
cub_errI(ii+1,z_cj),cub_errUS(ii+1,z_cj),cub_errUM(ii+1,z_cj),cub_errUSM(ii+1,z_cj),...
cub_timing_solver(ii+1,z_cj),cub_DOF(ii+1,z_cj)]=error_2D_squ_CEM(img,'tri10',0); toc;
end
%Refine model uniformly and find errors with lin
mdl=h_refine_square_domain(mdl); img=mk_image(mdl,1);
tic; fprintf(1,'H1 Lin');
[lin_errL2(nmesh+1,z_cj),lin_errH1(nmesh+1,z_cj),...
lin_errH1semi(nmesh+1,z_cj),lin_errI(nmesh+1,z_cj),lin_errUS(nmesh+1,z_cj),...
lin_errUM(nmesh+1,z_cj),lin_errUSM(nmesh+1,z_cj),lin_timing_solver(nmesh+1,z_cj),...
lin_DOF(ii+1,z_cj)]=error_2D_squ_CEM(img,'tri3',0); toc;
end
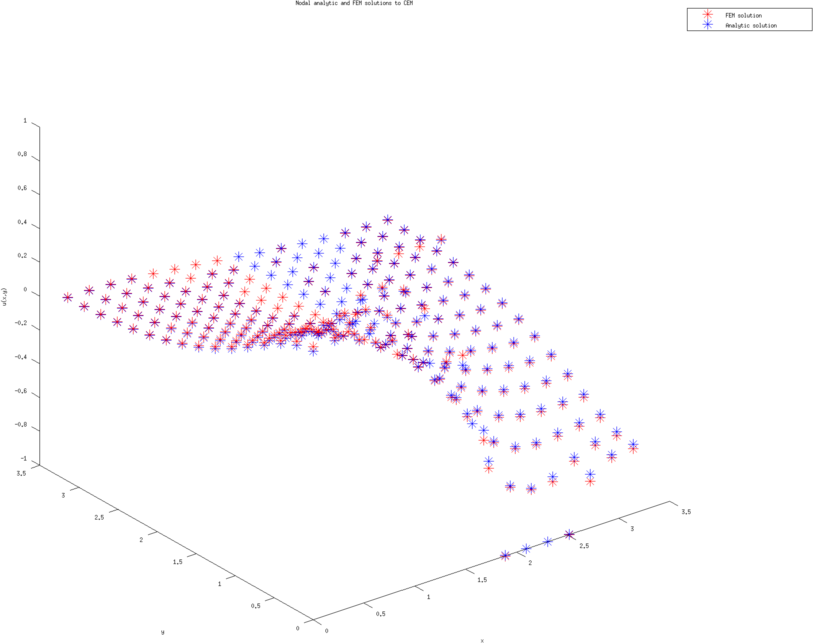
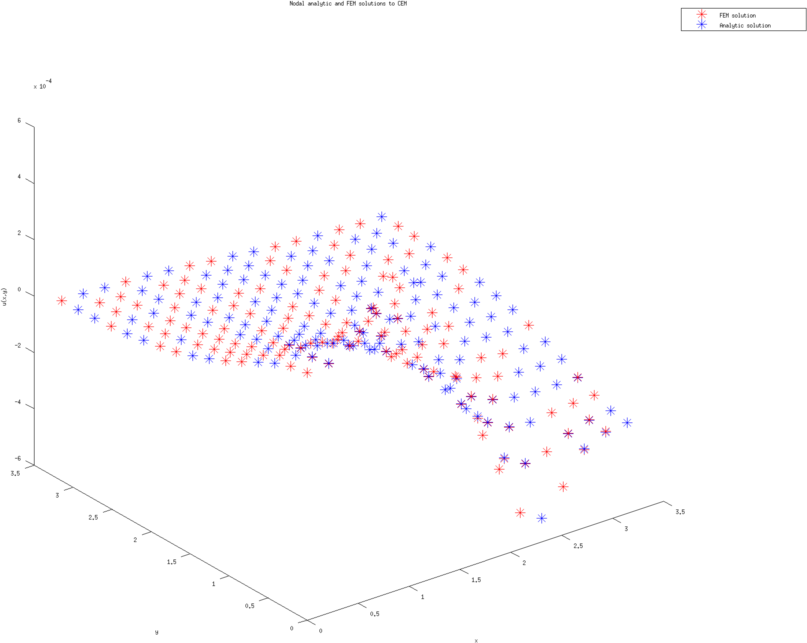
Figure: The left and right figure are the nodal potential values (with cubic approximation) using the analytic solution and finite element solution (on the coarsest triangulation.)
%Error rate fitting.
%Assume e = Ch^{p} => log(e) = A + p log(h) and h= C(1/2)^j
%log(e) = A+log(C) - j(p log(2))
%log(err) against jlog(2) will give gradient -p
n_plot=2; %First error 'not asymptotic'so disregard.
%Calculate the best fits for each z_c
for z_cj=1:length(z_c)
for j=1:nmesh
logh(j) = j*log(2);
logcon_func(j)=1;
logquad_errL2(j,z_cj) = log(quad_errL2(j,z_cj)); logquad_errH1(j,z_cj) = ...
log(quad_errH1(j,z_cj)); logquad_errUM(j,z_cj)=log(quad_errUM(j,z_cj));
logcub_errL2(j,z_cj) = log(cub_errL2(j,z_cj)); logcub_errH1(j,z_cj) = ...
log(cub_errH1(j,z_cj)); logcub_errUM(j,z_cj)=log(cub_errUM(j,z_cj));
end
%Extra data point for linear
for j=1:nmesh+1
loglin_errL2(j,z_cj) = log(lin_errL2(j,z_cj)); loglin_errH1(j,z_cj) = ...
log(lin_errH1(j,z_cj)); loglin_errUM(j,z_cj)=log(lin_errUM(j,z_cj));
end
%Linear
Alin=[logh',logcon_func'];
best_linL2(z_cj,:) = (Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*loglin_errL2(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
best_linH1(z_cj,:) = (Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*loglin_errH1(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
best_linUM(z_cj,:) = (Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Alin(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*loglin_errUM(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
%Quadratic
Aquad=[logh',logcon_func'];
best_quadL2(z_cj,:) = (Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*logquad_errL2(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
best_quadH1(z_cj,:) = (Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*logquad_errH1(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
best_quadUM(z_cj,:) = (Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Aquad(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*logquad_errUM(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
%Cubic
Acub=[logh',logcon_func'];
best_cubL2(z_cj,:) = (Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*logcub_errL2(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
best_cubH1(z_cj,:) = (Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*logcub_errH1(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
best_cubUM(z_cj,:) = (Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:))\...
Acub(n_plot:nmesh,:)'*logcub_errUM(n_plot:nmesh,z_cj);
end
%Plot all linear error rate on one graph against log(z)
figure; hold on;
plot(log10(z_c),-best_linL2(:,1),'ro');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_linH1(:,1),'bx');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_linUM(:,1),'md');
h =legend('L2','H1','UM','Location','NorthWest');
set(h,'FontSize',14);
xlab = xlabel('log(z)'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('Rate'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
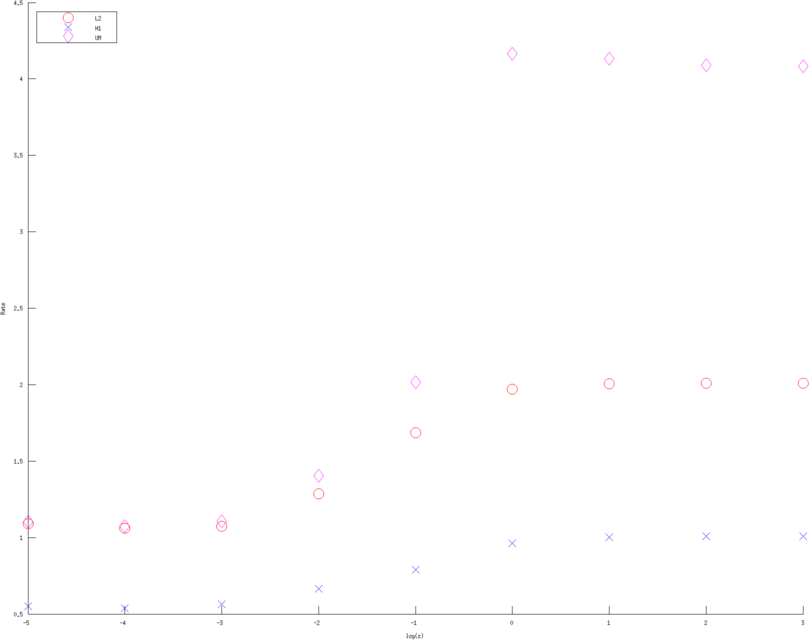
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance03a.png
%Plot all quadratic error rate on one graph against log(z)
figure; hold on;
plot(log10(z_c),-best_quadL2(:,1),'ro');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_quadH1(:,1),'bx');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_quadUM(:,1),'md');
h =legend('L2','H1','UM','Location','NorthWest');
set(h,'FontSize',14);
xlab = xlabel('log(z)'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('Rate'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance03b.png
%Plot all cubic error rate on one graph against log(z)
figure; hold on;
plot(log10(z_c),-best_cubL2(:,1),'ro');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_cubH1(:,1),'bx');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_cubUM(:,1),'md');
h =legend('L2','H1','I','US','UM','Location','NorthWest');
set(h,'FontSize',14);
xlab = xlabel('log(z)'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('Rate'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance03c.png
%Plot all L2 error rates against log(z) for each approx
figure; hold on;
plot(log10(z_c),-best_linL2(:,1),'ro');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_quadL2(:,1),'bx');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_cubL2(:,1),'g+');
h =legend('p=1','p=2','p=3','Location','NorthWest');
set(h,'FontSize',14);
xlab = xlabel('log(z)'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('Rate'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance03d.png
%Plot all H1 error rates against log(z) for each approx
figure; hold on;
plot(log10(z_c),-best_linH1(:,1),'ro');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_quadH1(:,1),'bx');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_cubH1(:,1),'g+');
h =legend('p=1','p=2','p=3','Location','NorthWest');
set(h,'FontSize',14);
xlab = xlabel('log(z)'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('Rate'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
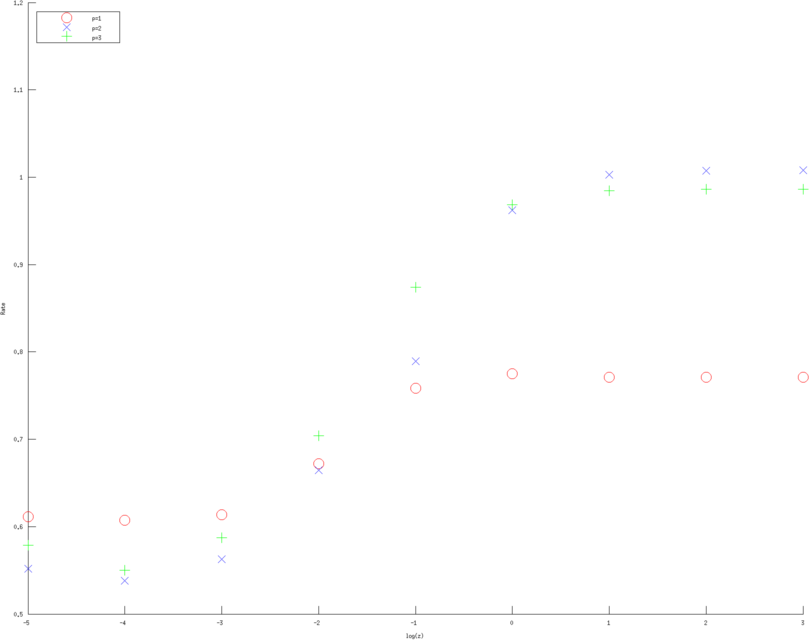
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance03e.png
%Plot all UM error rates against log(z) for each approx
figure; hold on;
plot(log10(z_c),-best_linUM(:,1),'ro');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_quadUM(:,1),'bx');
plot(log10(z_c),-best_cubUM(:,1),'g+');
h =legend('p=1','p=2','p=3','Location','NorthWest');
set(h,'FontSize',14);
xlab = xlabel('log(z)'); set(xlab,'FontSize',14);
ylab = ylabel('Rate'); set(ylab,'FontSize',14);
print_convert error_rates_contact_impedance03f.png
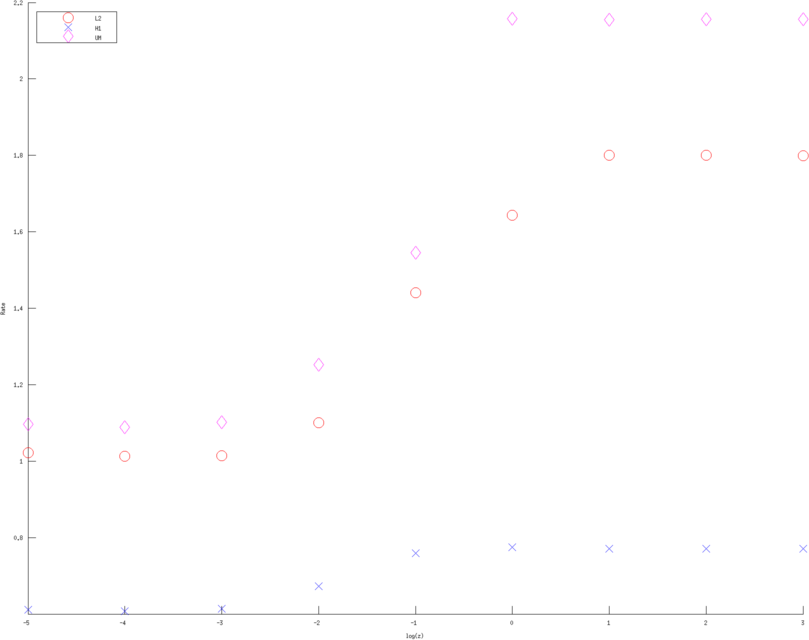 > >
 > >
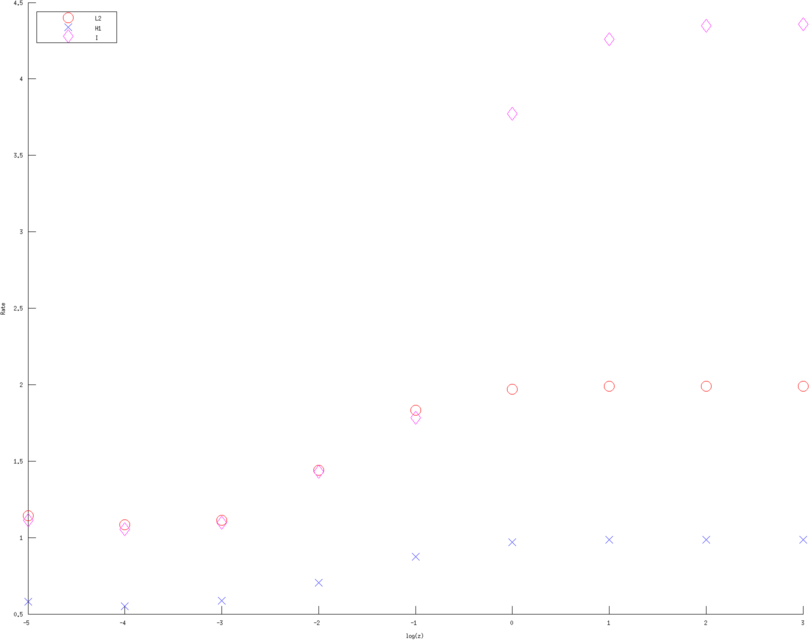 > >
Figure: Convergence rates (of various Error norms) as a function of contact impedance for various approximation order. Left, Middle, Right figure are using a linear, quadratic and cubic approximation respectively. Bue crosses are the H1 norm, Red circle the L2 norm and Purple diamons are the measured voltages in l2 norm 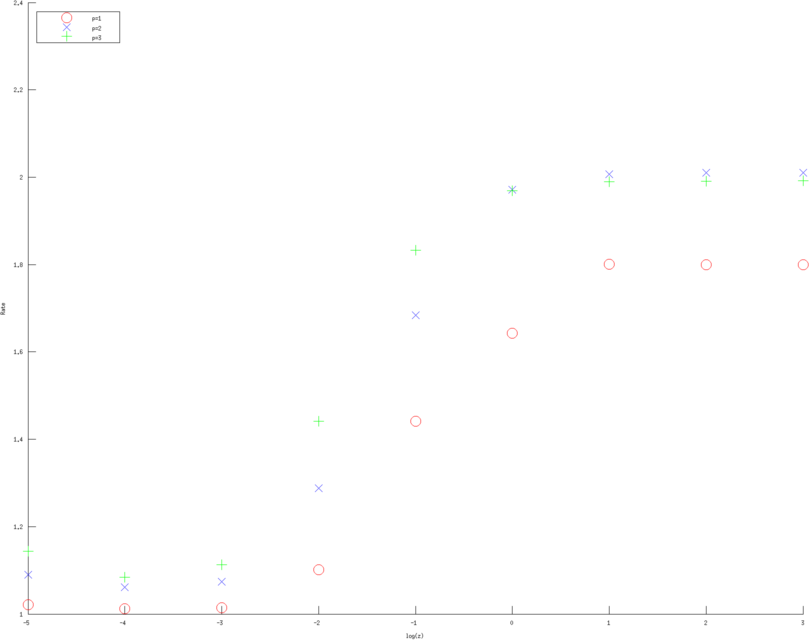 > >
 > >
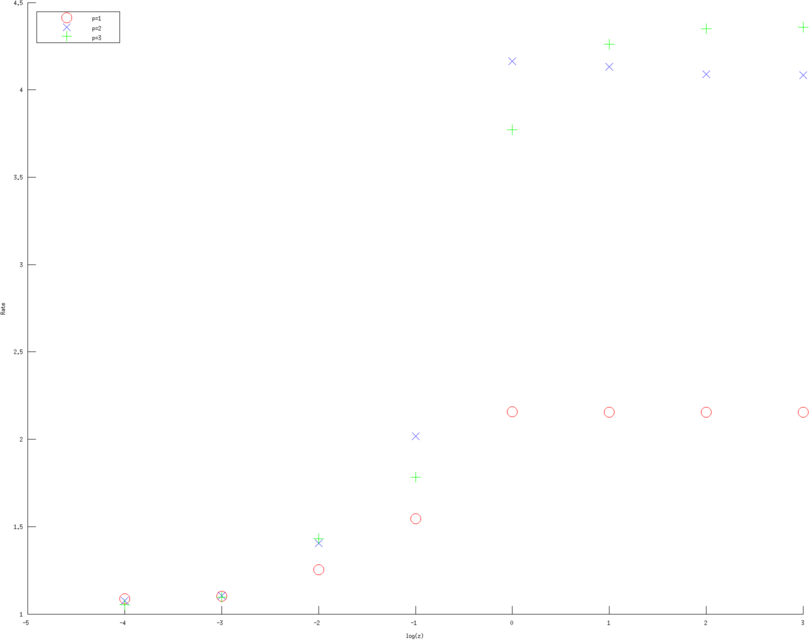 > >
Figure: Convergence rates (of various approximation orders) as a function of contact impedance for various Error norms. Left, Middle, Right figure are error rates estimate in H1 norm, L2 norm and l2 norm of measured voltages, linear, quadratic and cubic approximation respectively. Red circles are linear, Blue diagonal crosses are quadratic and Green verticle crosses are cubic approximations. |
Last Modified: $Date: 2017-04-28 12:58:02 -0400 (Fri, 28 Apr 2017) $ by $Author: michaelcrabb30 $